- Alt + Tab -- Switch between open applications.
- Alt + Shift + Tab -- Switch backward between open applications.
- Alt + Print Screen -- Create screenshot for the current program.
- Ctrl + Alt + Del -- Reboot/Windows task manager.
- Ctrl + Esc -- Bring up the start menu.
- Alt + Esc -- Switch between applications on the taskbar.
- F2 -- Rename selected icon.
- F3 -- Start find from the desktop.
- F4 -- Open the drive selection when browsing.
- F5 -- Refresh contents.
- Alt + F4 -- Close current open program.
- Ctrl + F4 -- Close window in program.
- Ctrl + Plus Key-- Adjust widths of all columns in WindowsExplorer.
- Alt + Enter -- Open properties window of selected icon or program.
- Shift + F10 -- Simulate right-click on selected item.
- Shift + Del -- Delete programs/files permanently.
This platform provides simple easily understandable study material for BTech CS/IT and BCA students.
Sunday, June 20, 2021
Microsoft Windows shortcut keys list
Computer shortcut keys
List of basic computer shortcut keys:
RECOMMENDED
·
Alt + F--File menu
options in the current program.
·
Alt + E--Edits options
in the current program.
·
F1--Universal help (for
any sort of program).
·
Ctrl + A--Selects all
text.
·
Ctrl + X--Cuts the
selected item.
·
Ctrl + Del--Cut selected
item.
·
Ctrl + C--Copy the
selected item.
·
Ctrl + Ins-- Copy the
selected item.
·
Ctrl + V--Paste the
selected item.
·
Shift + Ins -- Paste the
selected item.
·
Home -- Takes the user
to the beginning of the current line.
·
Ctrl + Home--Go to the
beginning of the document.
·
End -- Go to the end of
the current line.
·
Ctrl + End -- Go to the
end of a document.
·
Shift + Home --
Highlight from current position to beginning of the line.
·
Shift + End -- Highlight
from current position to end of the line.
·
Ctrl + (Left arrow) --
Move one word to the left at a time.
·
Ctrl + (Right arrow) --
Move one word to the right at a time.
Saturday, June 19, 2021
What is Database Management System? Explain various models of Database Management System in brief.
Database Management System (DBMS):
A database management system consists of collection of related data and refers to a set of programs for defining, creation, maintenance and manipulation of a database.
Function of DBMS:
- Defining database schema: it must give facility for defining the database structure also specifies access rights to authorized users.
- Manipulation of the database: The dbms must have functions like insertion of record into database updation of data, deletion of data, retrieval of data
- Sharing of database: The DBMS must share data items for multiple users by maintaining consistency of data.
- Protection of database: It must protect the database against unauthorized users.
- Database recovery: If for any reason the system fails DBMS must facilitate data base recovery.
Models of Database Management System
A Database model defines the logical design and structure of a database and defines how data will be stored, accessed and updated in a database management system.
While the Relational Model is the most widely used database model, there are other models too:
- Hierarchical Model
- Network Model
- Entity-relationship Model
- Relational Model
Hierarchical Model
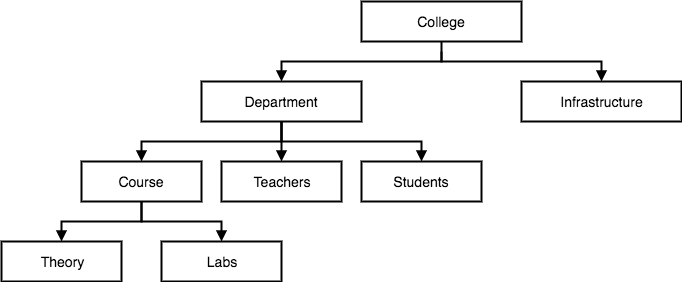
This database model organises data into a tree-like-structure, with a single root, to which all the other data is linked. The hierarchy starts from the Root data, and expands like a tree, adding child nodes to the parent nodes.
In this model, a child node will only have a single parent node.
This model efficiently describes many real-world relationships like index of a book, recipes etc.
In hierarchical model, data is organised into tree-like structure with one one-to-many relationship between two different types of data, for example, one department can have many courses, many professors and of-course many students.
Network Model
This is an extension of the Hierarchical model. In this model data is organised more like a graph, and are allowed to have more than one parent node.
In this database model data is more related as more relationships are established in this database model. Also, as the data is more related, hence accessing the data is also easier and fast. This database model was used to map many-to-many data relationships.
This was the most widely used database model, before Relational Model was introduced.

Entity-relationship Model
In this database model, relationships are created by dividing object of interest into entity and its characteristics into attributes.
Different entities are related using relationships.
E-R Models are defined to represent the relationships into pictorial form to make it easier for different stakeholders to understand.
This model is good to design a database, which can then be turned into tables in relational model(explained below).
Let's take an example, If we have to design a School Database, then Student will be an entity with attributes name, age, address etc. As Address is generally complex, it can be another entity with attributes street name, pincode, city etc, and there will be a relationship between them.
Relationships can also be of different types. To learn about E-R Diagrams in details, click on the link.

Relational Model
In this model, data is organised in two-dimensional tables and the relationship is maintained by storing a common field.
This model was introduced by E.F Codd in 1970, and since then it has been the most widely used database model, infact, we can say the only database model used around the world.
The basic structure of data in the relational model is tables. All the information related to a particular type is stored in rows of that table.
Hence, tables are also known as relations in relational model.
In the coming tutorials we will learn how to design tables, normalize them to reduce data redundancy and how to use Structured Query language to access data from tables.

Explain 3NF and BCNF. Also enlist their differences.
- It should be in second normal form
- It should not have any transitive dependencies for non-prime attributes
- 3NF states that no non-prime attribute must be transitively dependent on the candidate key of the relation. On the other hands, BCNF states that if a trivial functional dependency X -> Y exist for a relation; then X must be a super key.
- 3NF can be obtained without sacrificing the dependency of relation. However, dependency may not be preserved while obtaining BCNF.
- 3NF can be achieved without loosing any information from the old table whereas, while obtaining BCNF we may loose some information from the old table.
- Lossless decomposition can be achieved by 3NF. Lossless decomposition is hard to achieve in BCNF.
- It is comparatively easier to achieve.It is difficult to achieve.
- In 3NF there should be no transitive dependency that is no non prime attribute should be transitively dependent on the candidate key.In BCNF for any relation A->B, A should be a super key of relation.
What are the responsibilities of the DBA and the database designers?
Role, Duties and Responsibilities of database Administrator( DBA):
There are lots of role and duties of a database administrator (DBA). He is responsible for managing, securing and taking care of the database system. So before we start discussing the role and duties of DBA, we should understand who DBA is in actual and what is he meant for?
Who Is A DBA (Database Administrator)
A Database Administrator is a person or a group of person who are responsible for managing all the activities related to database system. This job requires a high level of expertise by a person or group of person. There are very rare chances that only a single person can manage all the database system activities so companies always have a group of people who take care of database system.Role Of DBA
In a nut shell, A DBA is the controller of everything related to database system. Now let us discuss what are the main role and duties of Database Administrator (DBA).
Role, Duties and Responsibilities of database Administrator( DBA)
Installing and Configuration of database: DBA is responsible for installing the database software. He configure the software of database and then upgrades it if needed. There are many database software like oracle, Microsoft SQL and MySQL in the industry so DBA decides how the installing and configuring of these database software will take place.
1. Deciding the hardware device
Depending upon the cost, performance and efficiency of the hardware, it is DBA who have the duty of deciding which hardware devise will suit the company requirement. It is hardware that is an interface between end users and database so it needed to be of best quality.
2. Managing Data Integrity
Data integrity should be managed accurately because it protects the data from unauthorized use. DBA manages relationship between the data to maintain data consistency.
3. Decides Data Recovery and Back up method
If any company is having a big database, then it is likely to happen that database may fail at any instance. It is require that a DBA takes backup of entire database in regular time span. DBA has to decide that how much data should be backed up and how frequently the back should be taken. Also the recovery of data base is done by DBA if they have lost the database.
4. Tuning Database Performance
Database performance plays an important role for any business. If user is not able to fetch data speedily then it may loss company business. So by tuning an modifying sql commands a DBA can improves the performance of database.
5. Capacity Issues
All the databases have their limits of storing data in it and the physical memory also has some limitations. DBA has to decide the limit and capacity of database and all the issues related to it.
6. Database design
The logical design of the database is designed by the DBA. Also a DBA is responsible for physical design, external model design, and integrity control.
7. Database accessibility
DBA writes subschema to decide the accessibility of database. He decides the users of the database and also which data is to be used by which user. No user has to power to access the entire database without the permission of DBA.
8. Decides validation checks on data
DBA has to decide which data should be used and what kind of data is accurate for the company. So he always puts validation checks on data to make it more accurate and consistence.
9. Monitoring performance
If database is working properly then it doesn’t mean that there is no task for the DBA. Yes f course, he has to monitor the performance of the database. A DBA monitors the CPU and memory usage.
10. Decides content of the database
A database system has many kind of content information in it. DBA decides fields, types of fields, and range of values of the content in the database system. One can say that DBA decides the structure of database files.
11. Provides help and support to user
If any user needs help at any time then it is the duty of DBA to help him. Complete support is given to the users who are new to database by the DBA.
12. Database implementation
Database has to be implemented before anyone can start using it. So DBA implements the database system. DBA has to supervise the database loading at the time of its implementation.
13. Improve query processing performance
Queries made by the users should be performed speedily. As we have discussed that users need fast retrieval of answers so DBA improves query processing by improving their performance.
Role, Duties and Responsibilities of database designers
The database designers are responsible to identify the data that to be stored in the database and choose suitable structures to store this data.
The database designer must have a solid working knowledge of the following:
- Database and Object-Oriented Analysis and Design techniques
- System Architecture, including Database and System performance tuning, as well as hardware and network workload balancing
- Database Administration
- an understanding of the implementation language and environment
Explain the concept of NoSQL Database and state its advantages over RDBMS.
Define the primary key. Explain the following relational operations with suitable example : (i) Select (ii) Project (iii) Union (iv) Intersection (v) Division
A primary key is a column -- or a group of columns -- in a table that uniquely identifies the rows in that table. For example, in the table below, CustomerNo, which displays the ID number assigned to different customers, is the primary key.
Codd originally defined eight relational
operators.
·
SELECT
·
PROJECT
·
UNION
·
INTERSECT
·
DIVIDE
SELECT
RESTRICTS the rows chosen from a table to
those entries with specified attribute values.
SELECT item
FROM stock_level
WHERE quantity > 100
constructs a new, logical table - an unnamed
relation - with one column per row (i.e. item) containing all rows from
stock_level that satisfy the WHERE clause.
PROJECT
Selects rows made up of a sub-set of
columns from a table.
PROJECT stock_item
OVER item AND description
UNION
Builds a relation consisting of all rows appearing in either or both of the two
relations.
For example, consider two relations, A and B,
consisting of rows:
A:
a B: a
=> A union B: a
b
e
b
c
c
e
INTERSECT
Builds a relation consisting of all rows appearing in both of the two
relations.
For example, consider two relations, A and B,
consisting of rows:
A: a B: a
=> A intersect B: a
b e
c
DIVIDE
Takes two relations, one binary and one unary, and builds a relation consisting
of all values of one column of the binary relation that match, in the other
column, all values in the unary relation.
A: a
x B: x
=> A divide B: a
a
y y
a
z
b
x
c
y
Transaction States in DBMS
States through which a transaction goes during its lifetime. These are the states which tell about the current state of the Transaction and also tell how we will further do processing we will do on the transactions. These states govern the rules which decide the fate of the transaction whether it will commit or abort.
These are different types of Transaction States :
Active State –
When the instructions of the transaction are running then the transaction is in active state. If all the ‘read and write’ operations are performed without any error then it goes to the “partially committed state”; if any instruction fails, it goes to the “failed state”.
Partially Committed –
After completion of all the read and write operation the changes are made in main memory or local buffer. If the the changes are made permanent on the Data Base then the state will change to “committed state” and in case of failure it will go to the “failed state”.
Failed State –
When any instruction of the transaction fails, it goes to the “failed state” or if failure occurs in making a permanent change of data on Data Base.
Aborted State –
After having any type of failure the transaction goes from “failed state” to “aborted state” and since in previous states, the changes are only made to local buffer or main memory and hence these changes are deleted or rolled-back.
Committed State –
It is the state when the changes are made permanent on the Data Base and the transaction is complete and therefore terminated in the “terminated state”.
Terminated State –
If there isn’t any roll-back or the transaction comes from the “committed state”, then the system is consistent and ready for new transaction and the old transaction is terminated.
Friday, June 18, 2021
Operating System
Introduction
An operating system acts as an intermediary between the user of a computer and computer hardware.
The purpose of an operating system is
to provide
an environment
in which a user
can execute programs conveniently and efficiently.
An operating system is software that manages
computer hardware.
The hardware must provide appropriate mechanisms to ensure the correct
operation of the computer system and to prevent user programs from interfering with the
proper operation of the system.
Operating System – Definition:
An operating system is a program that controls the execution of application programs and acts as an interface between the user of a computer and the computer hardware.
A more common definition is that the operating system is the one program running at all times on the computer (usually called the kernel), with all else being application programs.
An operating system is concerned with the allocation of resources and services, such as memory, processors, devices, and information.
The
operating system correspondingly includes programs to manage these resources, such as a
traffic
controller, a scheduler, a memory management
module, I/O programs, and a file system.
Functions of Operating system –
Operating system performs these
functions:
1. Convenience: An OS makes a
computer more convenient to use.
2. Efficiency: An OS allows the
computer system resources to be used efficiently.
3. Ability to Evolve: An OS should be constructed
in such a way as to permit the effective development, testing, and introduction
of new system functions at the same time without interfering with service.
4. Throughput: An OS should be
constructed so that it can give maximum throughput (Number of tasks per unit time).